About us?
Vitruvius is a specialized center in cardiovascular care in Mexico, with the ability to provide cutting-edge medical care, high quality, excellence and human commitment. Our team is made up of cardiologists, pediatric cardiologists, specialists in cardiovascular imaging, cardiac intervention, electrophysiology and arrhythmias, cardiac rehabilitation, endocrinology, pneumology, nephrology, for the care of children and adults, with the aim of integrating a group with a single center. Comprehensive and advanced resolution capacity in cardiovascular medicine.
)
Our Mission
To be a medical center of highly specialized excellence with the ability to prevent, diagnose and effectively treat patients with all kinds of cardiovascular diseases , providing humane treatment and high quality service.Our Vission
To be a multidisciplinary and reference center in cardiovascular medicine, to solve the cardiovascular problems that affect the population with great efficiency and quality in the service.
Leadership, Excellence, Commitment, Integrity, Honesty, Veracity, Humanism
Doctors
We have a team of specialists in the prevention, diagnosis and effective treatment of cardiovascular diseases.

Dr. José Luis Romero.
Cardiology, interventional cardiology, structural heart and endovascular peripheral cardiology.
View profileOur services
For our comprehensive approach and specialized teamwork we offer the following services:
Cardiometabolic check-up and for athletes

Medical consultation specialized in the area of pediatric and adult cardiology

Diagnostic studies in the area of cardiology by non-invasive and dynamic invasive imaging by cardiac catheterization

Early detection of diseases of the heart, aorta, peripheral vessels and congenital heart defects

Multidisciplinary management of cardiovascular diseases with different medical specialties

Advanced treatment of cardiovascular diseases

Forecast stratification of cardiometabolic diseases

Cardiac Rehabilitation

Innovative therapies in cardiovascular medicine and metabolism

Medical tourism
Diagnostic services
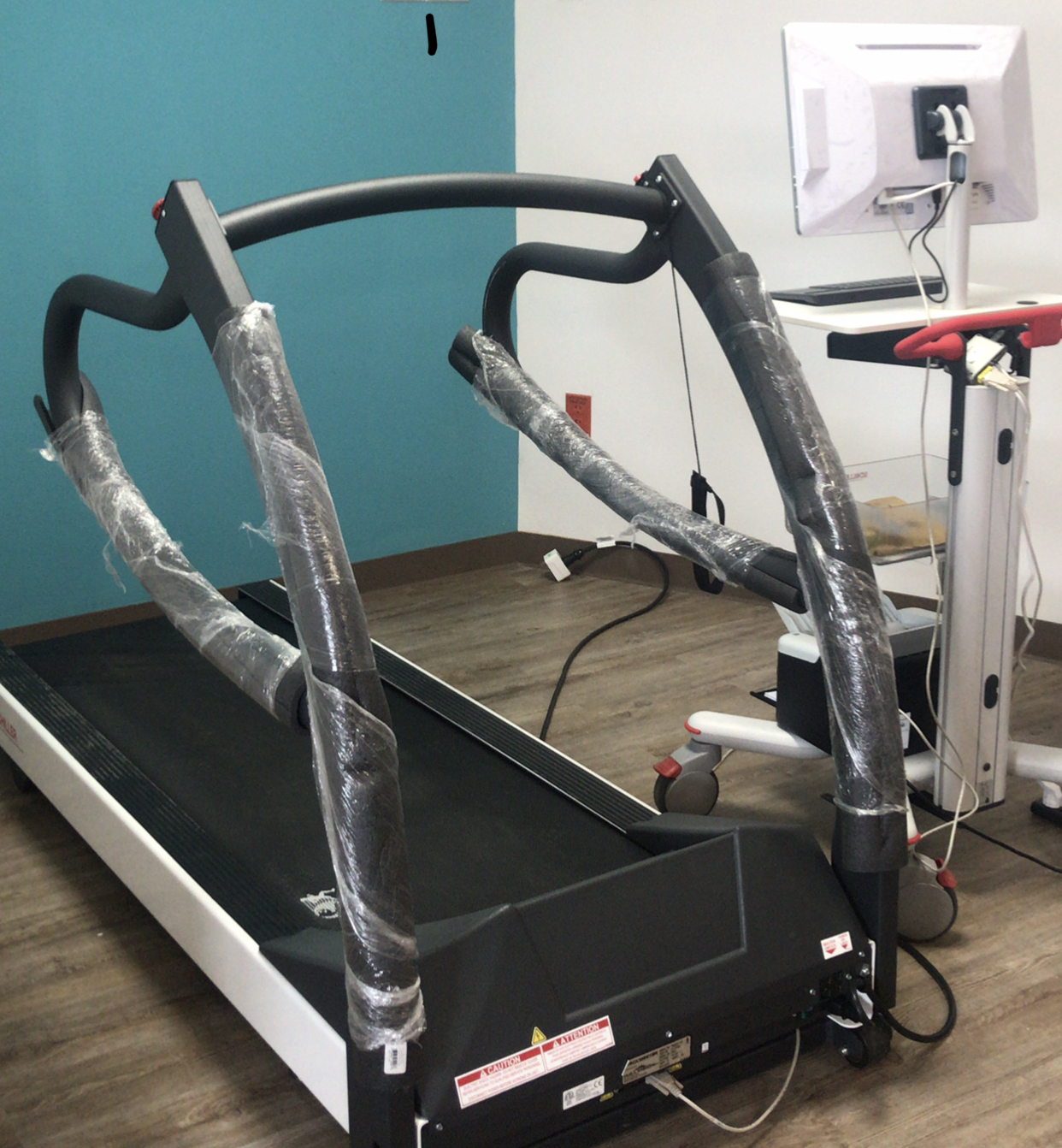
Treadmill stress testing
Doctors use the stress test to diagnose abnormalities in the blood supply to the heart arteries, irregular heartbeat or arrhythmias, or to detect symptoms such as chest pain or difficulty breathing related to exercise.
This test can be performed as a coronary disease detection study, such as check-up in healthy individuals with risk factors or as part of a cardiac rehabilitation program.
Instructions for patients:
1) Light breakfast on the day of the study
2) On the day of the study you can take your medications, except beta-blockers.
3) Go with comfortable clothes and tennis shoes.

Echocardiogram (Echo)
• Size and shape of the heart, and its cavities.
• Thickness and movement of the walls of the heart.
• Contraction and pumping capacity of the heart.
• Correct functioning of the heart valves.
• Evaluation of tumors, thrombi or infections inside the heart.
• Problems related to the outer covering of the heart (pericardium).
• Abnormalities in the structure of the heart or congenital defects.

Electrocardiographic monitoring (Holter)
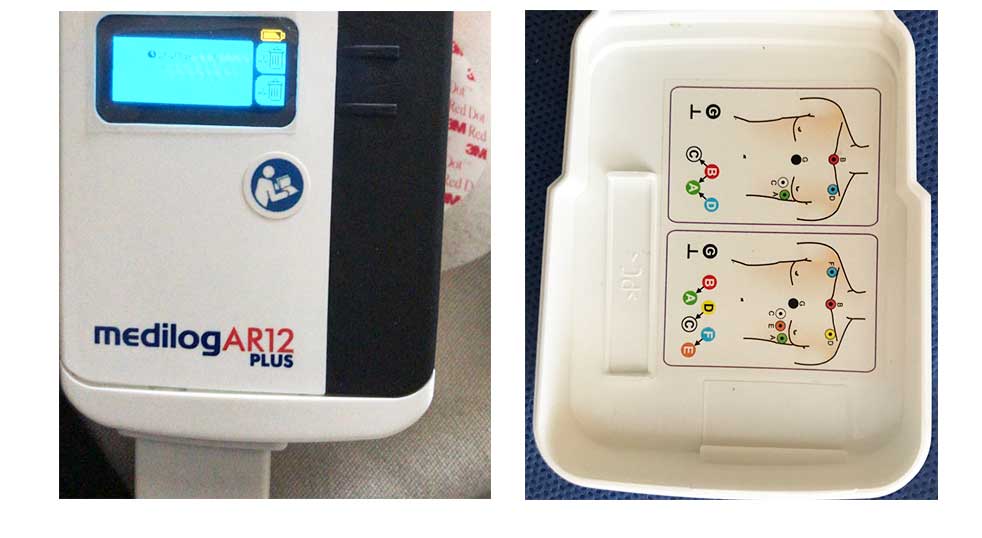
Ankle-brachial index (ABI)
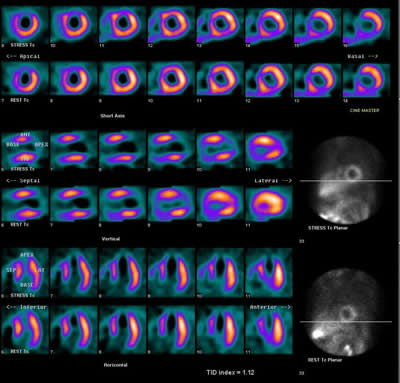
Cardiac SPECT
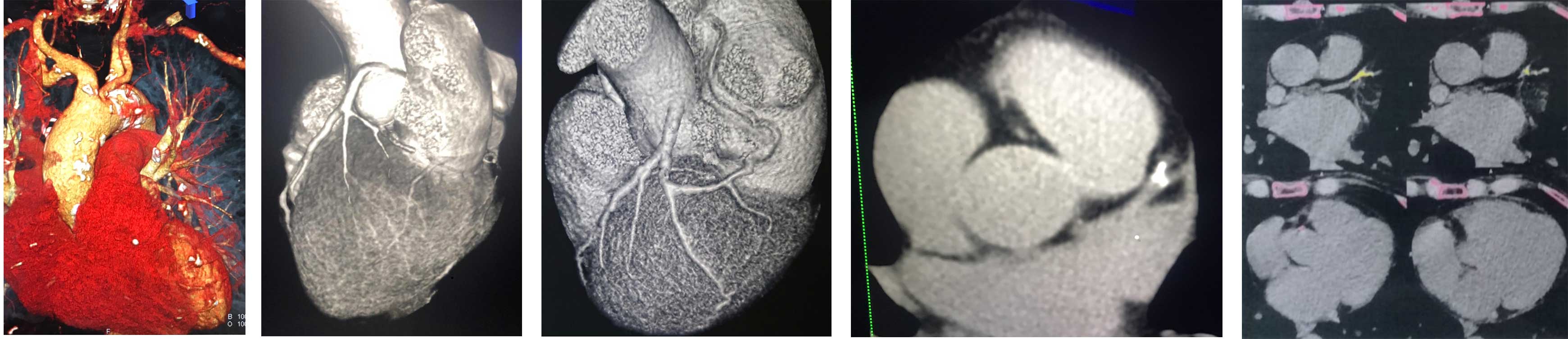
Cardiac tomography and coronary calcium score
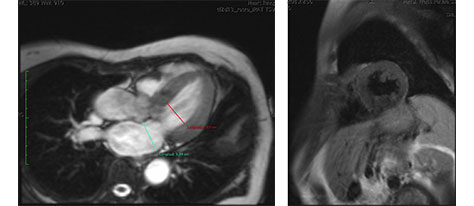
Cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR)
Interventional cardiology procedures
Cardiac catheterization
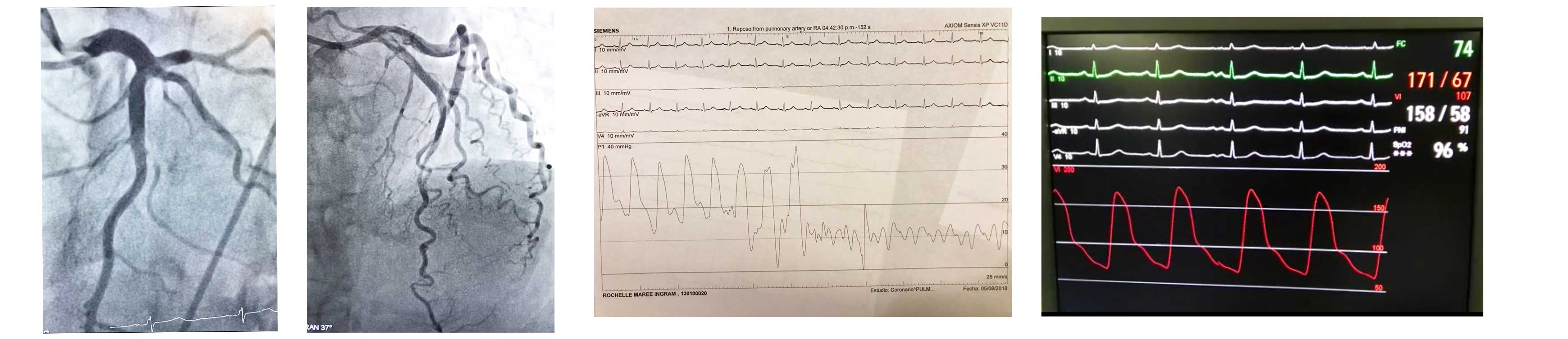
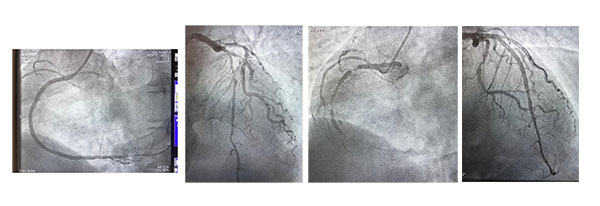
Coronary angioplasty (PTCA)
The benefits of coronary angioplasty are to increase blood flow through the narrowing artery, decrease chest pain (angina), increase in physical capacity limited by symptoms and decrease mortality.
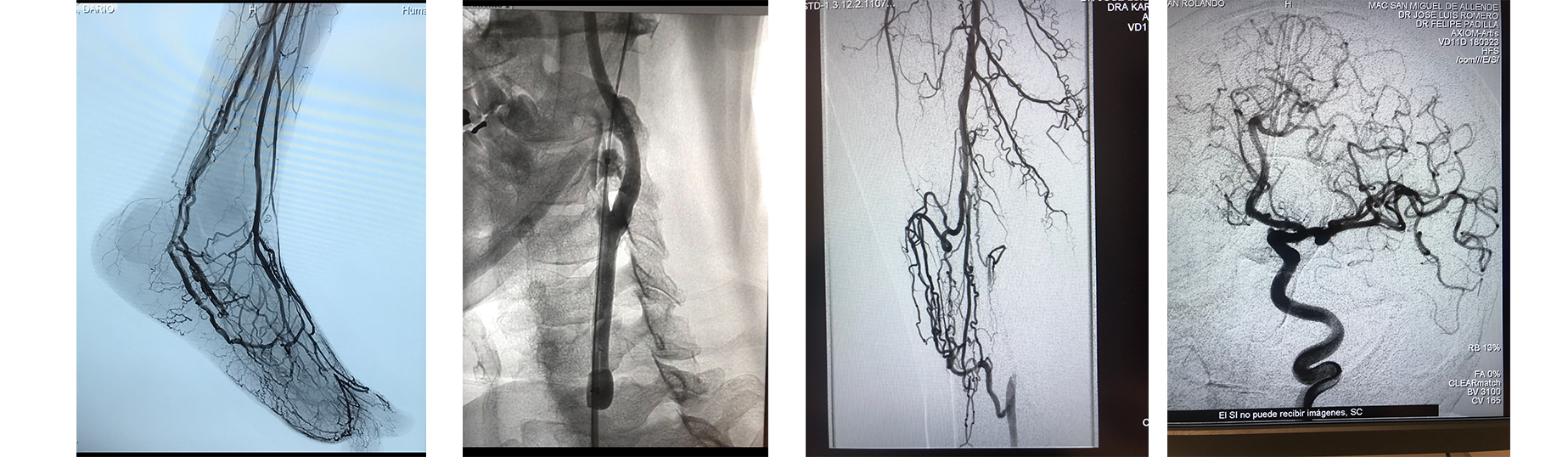
Peripheral angioplasty (PTA)
Structural and heart valves intervention
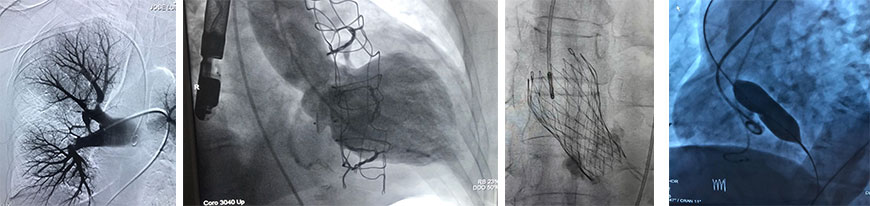
Electrophysiology procedures
Electrophysiological study

Radiofrequency ablation

Cryoablation
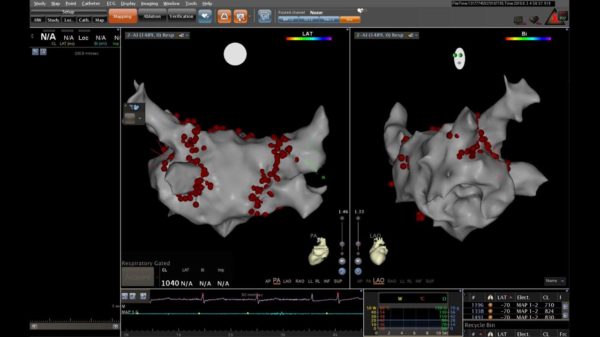
3D cardiac mapping
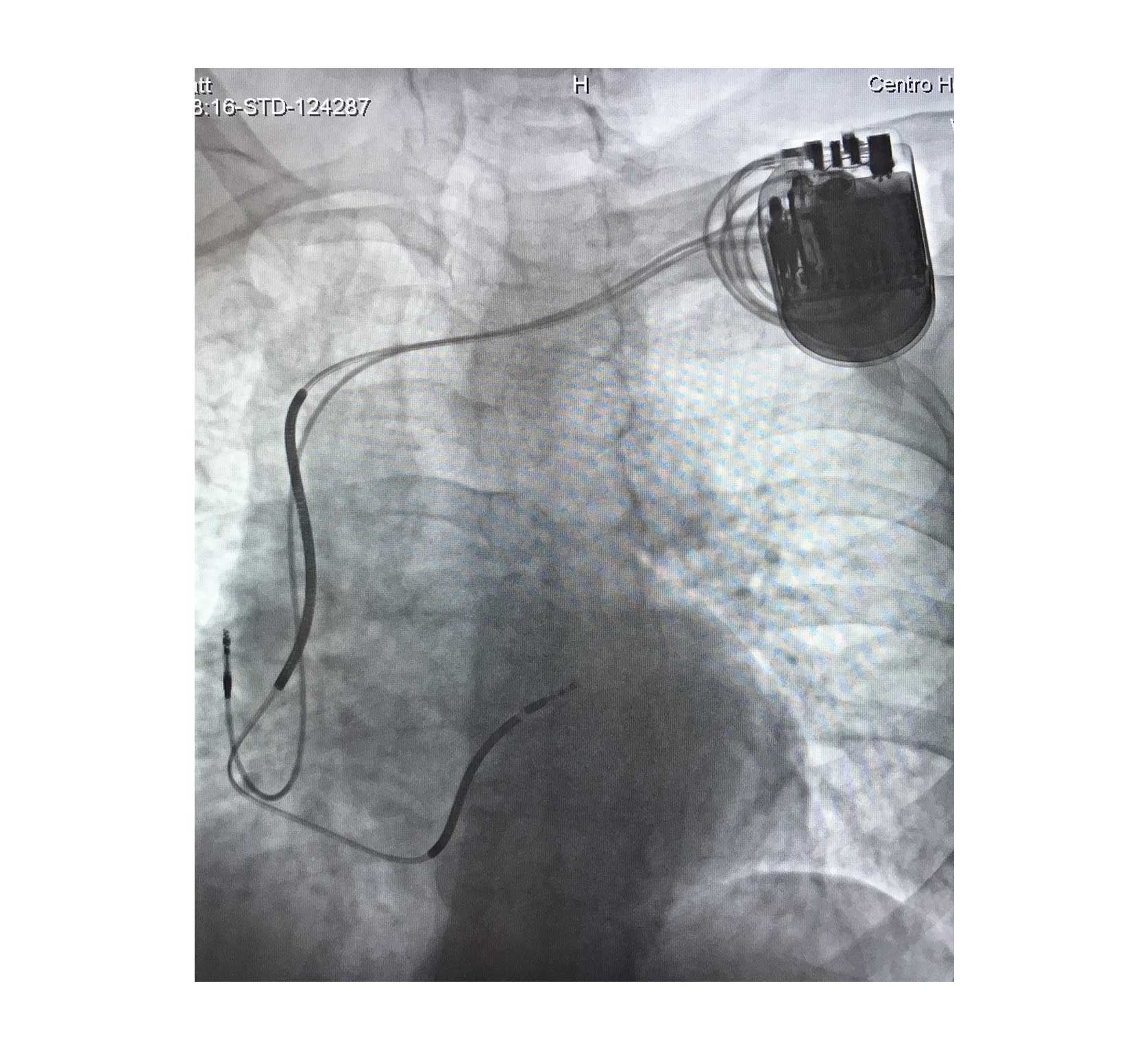
Pacemaker placement

Implantable cardiac defibrillator (ICD) placement
Cardiac and vascular surgery
Carotid endarterectomy

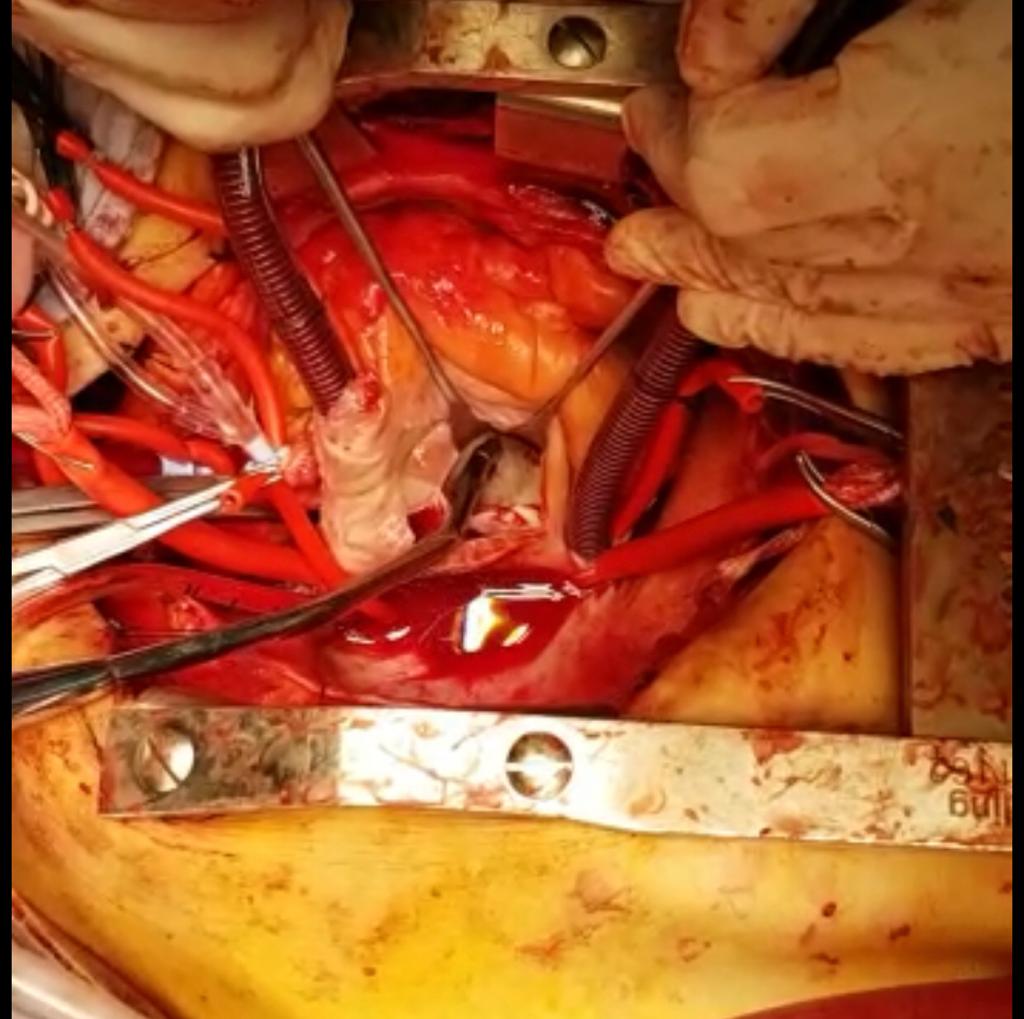
Coronary bypass graft surgery (CABG)
Bypass surgery is performed with an incision in the sternum, the heart beat is stopped with a special solution and the blood circulates through an extracorporeal circulation machine to allow the surgeon to place the blood vessel (bypass) grafts in the affected arteries. After placing the coronary bypass grafts, normal electric heart activity is restarted. This technique can be performed minimally invasive through small incisions in the thorax and without stopping the heart in selected cases, or as a hybrid procedure, combining cardiac catheterization techniques and stenting.
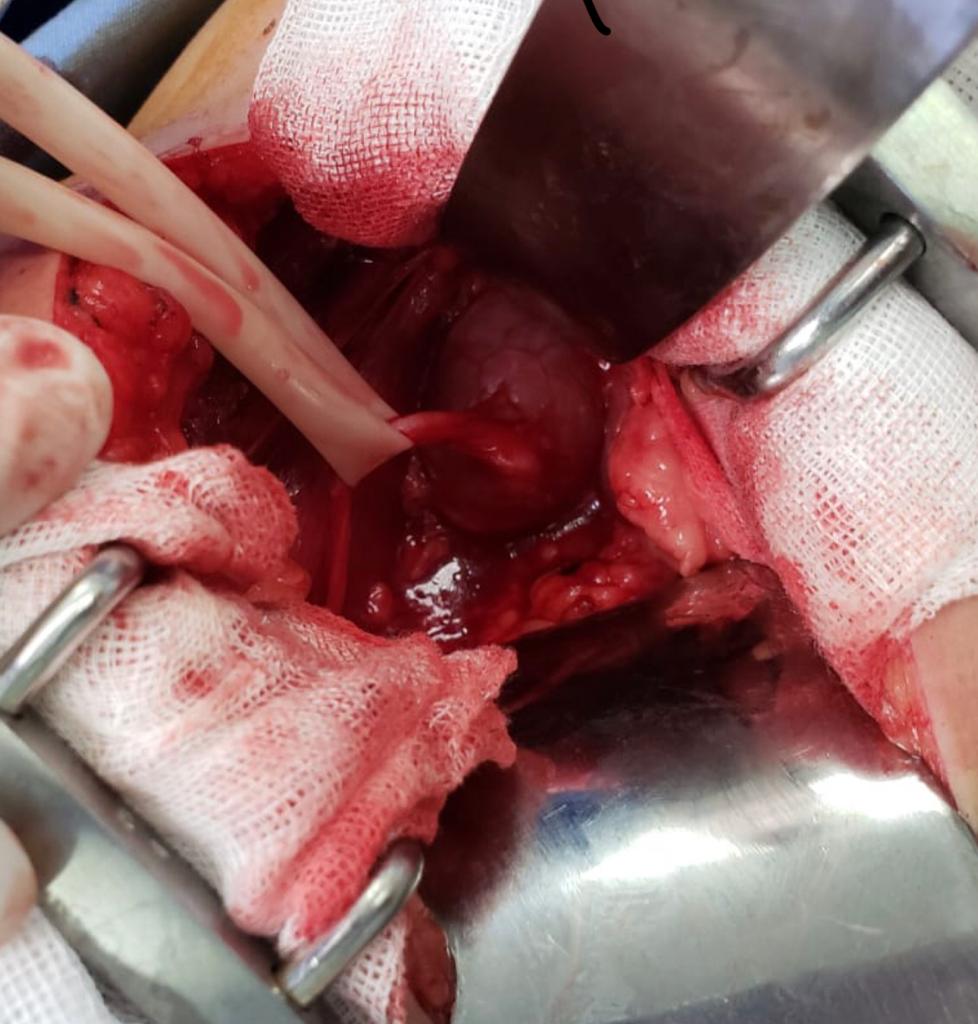
Heart valvular surgery
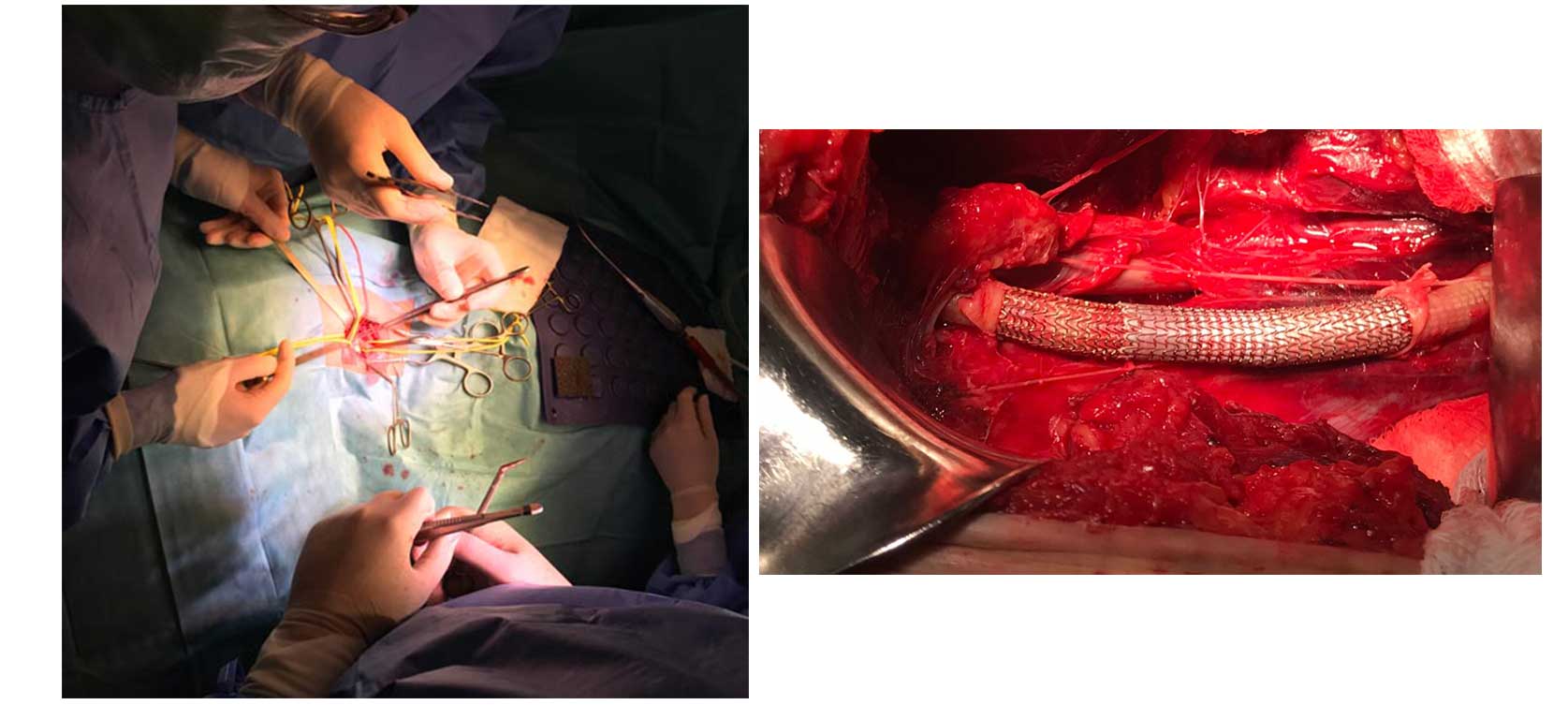
Peripheral vascular surgery
Cardiac Rehabilitation
Cardiac rehabilitation programs (CRP) are a set of multidisciplinary activities: medical, physical and psychosocial training that aim to provide medical assistance to patients with heart disease, especially after a myocardial infarction, angioplasty, cardiac surgery, as well as patients who have seen their functional capacity diminished due to other cardiopulmonary diseases such as heart failure.
The services include a medical evaluation, prescription of exercise, modification of risk factors, education and counseling of patients. These programs are designed to limit the harmful physiological and psychological effects of heart disease, reduce the risk of sudden death or reinfarction, control cardiovascular symptoms, stabilize or reverse the disease and improve the psychosocial state.